Developing with Visual Studio Code#
Visual Studio Code is a popular open-source code editor that is widely used for developing Python applications. It is a lightweight and powerful code editor that is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux. It has built-in support for Python, and it is easy to install and configure. This section provides a brief overview of how to set up Visual Studio Code for developing Python applications and how to use it to work BEC.
Installation#
On PSI-maintained Linux computers, Visual Studio Code is already installed and can be loaded using the command module add VSCode/<version> and then code to start the application. At the time of writing, the latest version is 1.73.1, and it can be loaded using the command module add VSCode/1.73.1.
If you want to install it on your own computer or on a machine that is not PSI-maintained, you can download it from the official website.
Extensions#
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) relies heavily on extensions to provide additional functionality. You can install extensions from the Extensions view (⇧⌘X on MacOS, Ctrl+Shift+X on Windows and Linux). The following extensions are recommended for developing Python applications with BEC:
Python (provided by Microsoft)
Black Formatter (provided by Microsoft)
Configuration#
Appearance#
You can customize the appearance of Visual Studio Code by opening the command palette (⇧⌘P on MacOS, Ctrl+Shift+P on Windows and Linux) and typing “color theme”. You can then select the color theme that you want to use.
Python interpreter#
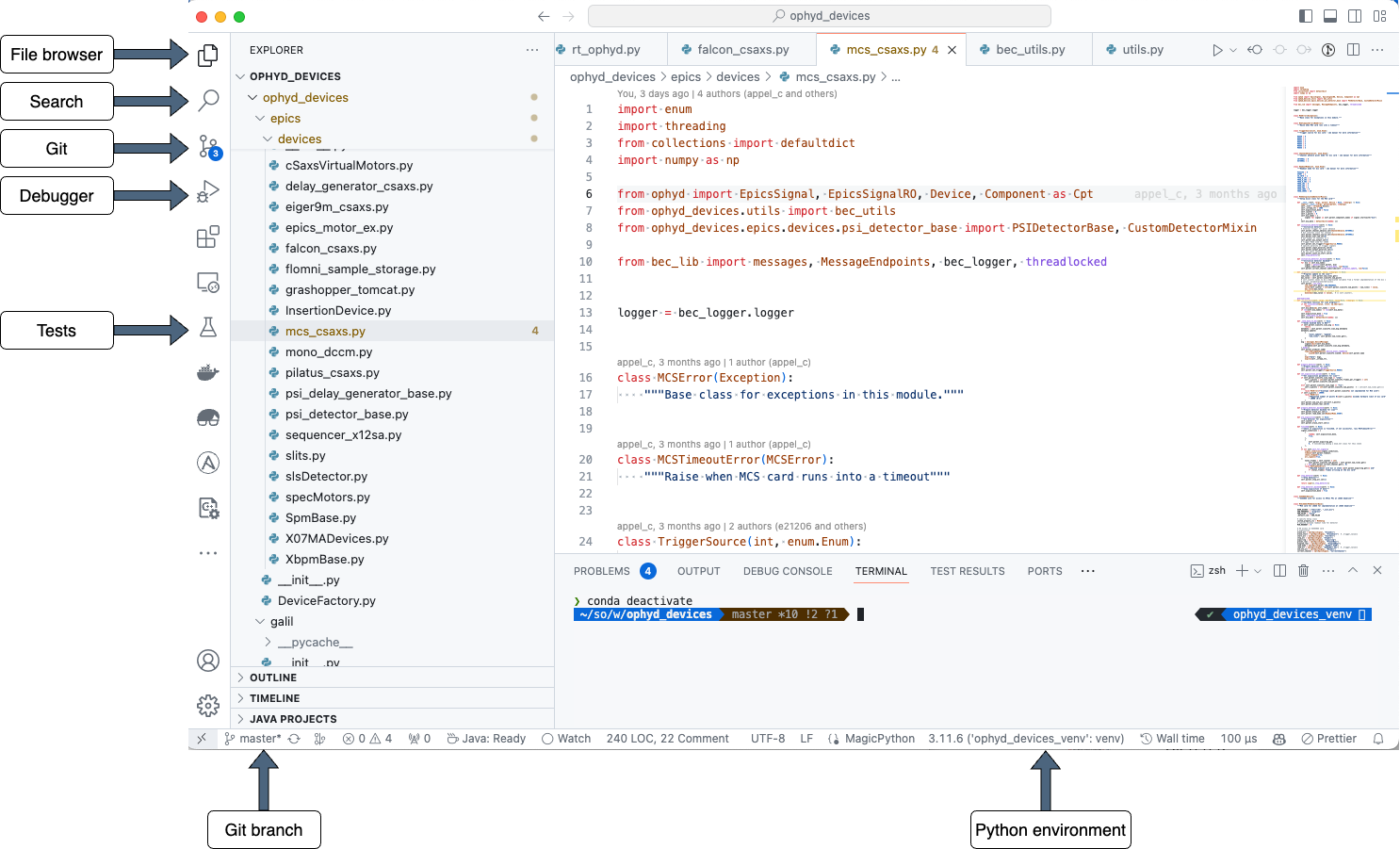
After installing the Python extension, you can configure the Python interpreter by clicking on the Python version in the bottom right corner of the window (see the figure below). You can select the Python interpreter that you want to use for your project. If you are working with a virtual environment, you can select the Python interpreter from the virtual environment. If you are working with a conda environment, you can select the Python interpreter from the conda environment.
Common keyboard shortcuts#
The following keyboard shortcuts are commonly used in Visual Studio Code:
Ctrl+Shift+P(Windows, Linux) orCmd+Shift+P(MacOS): Open the command paletteCtrl+P(Windows, Linux) orCmd+P(MacOS): Quick open file by nameCtrl+Shift+N(Windows, Linux) orCmd+Shift+N(MacOS): Open a new windowCtrl+Shift+W(Windows, Linux) orCmd+Shift+W(MacOS): Close the current windowCtrl+Alt+Shift+Up(Windows, Linux) orCmd+Option+Shift+Up(MacOS): Add cursor above (multi-cursor)Ctrl+Alt+Shift+Down(Windows, Linux) orCmd+Option+Shift+Down(MacOS): Add cursor below (multi-cursor)
More keyboard shortcuts can be found in the official documentation or by opening the command palette and typing “keyboard shortcuts”.
Hint
The most important keyboard shortcut in VSCode is Ctrl+Shift+P (Windows, Linux) or Cmd+Shift+P (MacOS), which opens the command palette. You can use the command palette to access all the functionality of VSCode, including opening files, running commands, and installing extensions.
Working with BEC#
Open a folder#
To open a folder in Visual Studio Code, click on the “File” menu and select “Open Folder”. You can then select the folder that you want to open. This will open the folder in the Explorer view, and you can see the files and folders in the folder.
VSCode is largely based on the concept of “workspaces”. A workspace is a collection of one or more folders that are opened in VSCode. When working on BEC, it is recommended to open either the bec root directory or a specific service directory, e.g. bec/bec_lib or bec/device_server.
Starting a service from VSCode#
Before you start a service from VSCode, you need to ensure that the service is installed and that the environment is set up correctly.
Note
Some services such as the device server, the file writer and the scan server are actively checking if another instance of the service is already running. If you start a service that is ought to be unique, you will get an error message saying that another instance of the service is already running. Please make sure to stop the service before starting a new instance.
All services provide a launch.py file in their cli directory, e.g. bec/bec_server/bec_server/device_server/cli/launch.py. You can start the service by opening the launch.py file and then clicking on the “Debug” button in the top right corner of the window. This will start the service in debug mode, and you can see the output of the service in the Debug Console.